What is LED and Why Is It Important?
LED is used in many devices including printed circuit boards. A transparent cover is used to encapsulate an LED that allows emitted light to escape. The conductor is often used in printed circuit boards (PBCs) due to many advantages.
Here you will learn about the inner workings of the LED PCB. You will also learn about the importance and fabrication of LED PCB and Flex PCB LED in this blog post.
Understanding the Working of LED PCB
An LED, or light emitting device, produces light when current is passed through it. The light is produced due to a recombination of current-carrying particles, namely electrons and holes within the material. A functional PCB contains many LEDs that are soldered on the board.
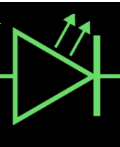
The LED PCB symbol conforms to the standard diode symbol but includes two small arrows indicating the emission of light, as shown in the figure below.
LED PCBs contain a p-n junction that is heavily doped. The devices emit colored light depending on the semiconductor material and doping concentration used. The type of semiconductor material and the amount of doping determines the specific spectral wavelength at which the device emits light.
When a diode is forward-biased, the electrons in the p-type region are depleted, while holes in the n-type region build up. This leads to an increase in the concentration of minority charge carriers at the junction.
The recombination of charges accelerates the release of photons which results in electroluminescence. LEDs glow due to this release of photons, unlike other diodes that glow due to intense heat.
Electroluminescence Property of LED PCBs
Electroluminescence is a particular property of LED PCBs. The light is created when the electrons pass through the diodes. With an LED, the intensity of the emitted light increases as the forward voltage passing through it rises, until it reaches its maximum.
In LED PCBs, the electrons are limited to certain bands of energy. The difference between the bands of energy affects the intensity of the photons that are emitted when the electric current is passed through it. The intervals are also known as wavelengths that determine the electroluminescence property of the LED.
Different colors of light are produced by various semiconductor materials with varying energy bands or bandgaps. To achieve the desired wavelength (color) of emitted light, the composition of the active region in a light-emitting device can be adjusted.
The primary substrate material for LED PCBs is aluminum, but alternatives such as FR4, polyimide, aluminum nitride, aluminum oxide, and copper are also used.
On the other hand, Flex PCB LEDs are constructed from a thin, thermally conductive material that facilitates rapid heat dissipation when compared to conventional PCB boards. Each material has distinct thermal performance properties that influence the heat transfer characteristics of flex PCBs.
Choosing the right substrate material depends on the specific requirements of the LED application. Factors such as thermal management, flexibility, cost, and power considerations influence the selection process. Engineers and designers carefully evaluate these factors to optimize the performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of LED PCBs for diverse applications.
Heat Dissipation in LED PCBs
Effective heat dissipation is crucial to ensuring the reliability and longevity of LEDs. LED PCBs must include heatinks to efficiently remove the heat generated during operation. The operating temperature of the LEDs has a significant impact on their performance, as higher temperatures can speed up degradation and shorten their lifespan. Therefore, thermal management is vital to ensure the successful implementation of LEDs.
To handle heat management, flex PCB LED products utilize a range of distinctive heat sink designs and configurations. With the help of advances in materials, manufacturers are now able to create LED bulbs that resemble traditional incandescent bulbs in shape and size. Regardless of the type of heat sink design employed, all flex PCB LED products that have attained the ENERGY STAR certification undergo testing to guarantee efficient heat management that preserves light output throughout the rated lifespan of the product.
What are the Applications of LED PCBs?
A single LED PCB may consist of multiple LEDs since a single one does not produce sufficient light on its own. Soldering multiple LEDs together is more efficient compared to using individual LED PCBs.
Aluminum-based LED PCBs provide an optimal solution for these applications, as they possess exceptional heat transfer abilities.
The semiconductor devices also find wide-ranging applications in traffic and transportation, spanning from stoplights to vehicles. In automobiles and trucks, these LEDs are utilized in headlights, brake lights, and indicators, among other applications. LED PCBs are employed in traffic and signal lighting, street lighting, and highway tunnel lighting. They are used in airports for illumination of the runway and towers. Similarly, other modes of transportation rely on LED PCBs for similar purposes.
Due to their durability and exceptional heat transfer capabilities, many lighting tools used in surgical and medical examinations employ high-powered LED lights with aluminum PCBs. These LEDs ensure that the medical equipment remains functional, even when treating numerous patients at a time. Medical scanning technologies frequently use aluminum PCB-based LED lights as well.
In recent years, most mobile devices, including tablets, smartphones, and laptops, have transitioned to using surface-mount devices (SMDs) to reduce weight and enhance heat dissipation properties. LED PCBs are frequently found in telecommunications equipment due to the thermal requirements of the surrounding machinery.
Finally, LED is used in consumer and commercial lighting applications. LED lights are superior to conventional tungsten and incandescent lights. Lighting solutions with LED PCBs draw much less power resulting in a reduction in energy demands. Moreover, LED lighting is also more efficient in handling heat making it durable and longer-lasting than alternative lighting solutions.
Conclusion
LED is used in PCB the fabrication process due to many advantages. The LED PCB process is used in the assembly of devices in various industries. The PCB fabrication process is used in aviation, automobiles, lighting, and various other industries.
LED PCB designs are used for the assembly of devices such as computers, HDTVs, lighting, telecommunication equipment, medical devices, and other products—the fabrication process results in devices that are more efficient in handling heat resulting in efficient operations.
For more information on LED PCB Or flex PCB fabrication